This tutorial is based on Deep Learning: Foundations and Concepts and also Ping Wang’s previous work with students, parents, teachers and researchers in AI outreach (NASA-funded HiRISE+AI and NSF-funded Planet+AI) since 2021, targeting high school students and the general public at large.
MACHINE LEARNING
Machine learning is computationally-focused statistical learning. Most machine learning problems belong to one of the following three main categories: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. In supervised learning, each data point is labeled or associated with a category. In unsupervised learning, data points have no labels associated with them. In reinforcement learning, the algorithm gets to choose an action in response to each data point. Supervised learning can come in two distinct forms: (1) classification whenver we use the data to predict categories, and (2) regression whenever we use the data to predict real values.
DEEP LEARNING
Deep learning uses artificial neural networks trained with big data to solve many problems in many fields, including computer vision and natural language processing. Deep learning is based on neural networks with representation learning. Large language models (LLMs) are neural networks with trillions of parameters. Artificial neural networks is also called neural networks. The deep learning revolution started around Convolutional Neural Networks and GPU-based computer vision.
WHAT IS A FUNCTION
In mathematics, a function from a set X to a set Y assigns to each element of X exactly one element of Y.
A function relates each element of a set with exactly one element of another set. Thus,
(1) A function must work for every possible input value.
(2) It has only one relationship for each input value.
Also,
(1 )The set X is called the Domain.
(2) The set Y is called the Codomain.
(3) The set of elements that get pointed to Y (the actual values produced by the function) is called the Range.
ORDERED PAIRS
The input and output of a function can be written as an ordered pair, such as (3,9).
The input always comes first; and the output second: (x, f(x)).
Ordered pairs are also called 2-tuples. Ordered pairs are also coordinates. we can create functions with ordered pairs.
DOT PRODUCTS
A vector has magnitude and direction. The dot products of two vectors A and B is a key operation in algebra and also in geometry.
Dot Products in Algebra:
If A = (a1, a2, …, an) and B = (b1, b2, …, bn), then the dot product of A and B = a1b1 + a2b2 +… + anbn
Examples:
Let A=(1,2,3), B=(3,2,1). The dot product of A and B = 1 * 3 + 2 * 2 + 3 * 1 = 10
Let C=(1,2,3), D=(3,-2,1). The dot product of C and D = 1 * 3 + 2 * (-2) + 3 * 1 = 2
And See the folowing figure, a=(-6, 8), b=(5, 12), the angle θ between a and b is 59.5o
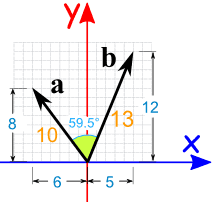
Credit: Image from https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/vectors-dot-product.html
The dot product of a and b can also be calculated by this way:
a · b = |a| x |b| x cos(θ) where |a| is the magnitude of vector a, |b| is the magnitude of vector b, and θ is the angle between a and b.
Thus, a·b = |a| x |b| x cos(θ) = 10 * 13 * cos(59.5o) = 65.98
If the magnitude of the two vectors and the angle between them is not known, we can calculate the dot product in algebraic way:
a·b = a1b1 + a2b2. In this case, we multiply the vector length as they are projected onto the x-axis and y-axis of the Cartesian plane.
Thus, a·b = (-6) * 5 + 8 *12 = 66
Both methods come up with the almost same result (afeter rounding). Above is about calculating the dot product for vectors in a 2-dimensional space. A similar approach can be used to calculate the dot product for vectors in a n-dimensional space.
In Convolutional Neural Networks, a dot product is defined as being a sum of products by multiplying element-wise and then add them all together. The convolution operation in images ia a matrix where each entry is a dot product.
The dot product is a measure of how closely two vectors algin in terms of the directions they point.
VECTOR SPACE
A vector space, also called a linear space, is a set whose elements, often called vectors, can be added together and multiplied (“scaled”) by numbers called scalars. The concept of vector spaces is fundamental for Linear Algebra, which provides a concise and way for manipulating and studying systems of linear equations. Vector spaces are charaterized by their dimensions, which specifies the number of independent directions in the space. There are two axioms about a vector space: (1) the sum of two vectors must be a vector, and (2 )the multiple of a vector by a scalar must be a vector.
LINEAR EQUATIONS
Here’s a problem: Find x1, x2, x3 ∈ R that solves the system of linear equations
x1 + 2x2 + 3x3 = 8
4x1 + 5x2 + 6x3 = 11
7x1 + 8x2 + 9x3 = 7
The problem above can be reworded as the following matrix equation:
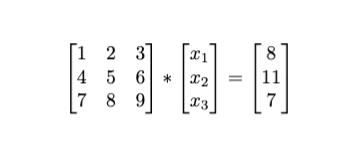
LINEAR REGRESSION AS A SINGLE LAYER NEURAL NETWORK
The easiest regression model is called linear regression. Linear regression describes a target variable with a linear combination of features. In a linear regression, each input is connected to the output. The inputs are x1, x2, …, xd. We refer to d as the number of inputs or the feature dimensionality in the input layer. The output of the network is o1. We only have one output neuron. Linear regression can be taken as a single layer fully-connected neural network, each feature is represented by an input neuron, all of which are connected directly to the output.
We can build a single-layer neural network adn train it with the iris dataset and solve a classification problem. The iris dataset has dimensionality 4, namely sepal_length, sepal_width, petal_length, and petal_width. the target labels are one of the 3 classes of iris, namely iris settosa, iris versicolor, and iris virginica respectively. The neural network has input layer, output layer and 1 hidden layer. The input layer has 4 nodes, which matches the dimensionality of 4 features. The output layer has 3 nodes to match one-hot encoding of the target labels.
References:
Deep Learning: Foundations and Concepts